How to install and use Docker on Ubuntu 24.04
This guide will walk you through
the installation of Docker on Ubuntu 24.04, and
basic commands to get you started with Docker containers.
What we are going to cover
Prerequisites
Ensure your system meets the following requirements:
Ubuntu 24.04.2 64-bit system
4 GB of RAM (recommended for better performance)
20 GB of free storage (minimum for Docker and container images)
Kernel version 3.10 or higher (default for Ubuntu 24.04.2)
Virtualization enabled (if running in a virtualized environment like VMware or Hyper-V)
Internet connection for downloading packages
Sudo privileges or root access
If these prerequisites are valid, you will be able to install Docker on:
a computer natively running Ubuntu 24.04
a VM running on a local computer
a VM running in the CloudFerro Cloud cloud
Prerequisites for the cloud version of Docker
No. 1 Account
To run Docker on a VM in the cloud, you need your own cloud account. See article: Registration and Setting up an Account.
No. 2 A VM running Ubuntu 24.04
Create a VM by following this or a similar article: How to create a Linux VM and access it from Linux command line on CloudFerro Cloud
In the Source option, select Ubuntu 24.04 and then “Ubuntu 24.04 LTS”:
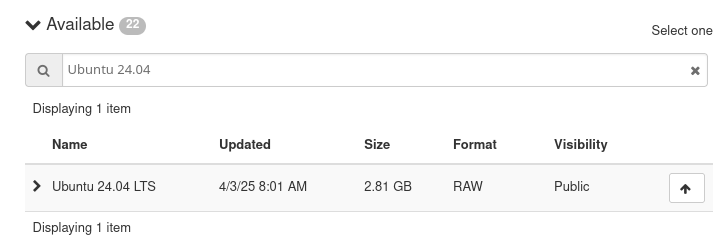
Fig. 30 Selecting Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
Choose a flavor such as eo2a.large or larger.
No. 3 Is lsb_release running?
The lsb_release -cs command returns the codename for your Ubuntu version. For Ubuntu 24.04, this is noble.
lsb_release -cs
No LSB modules are available.
noble
If the command is not available, install it using:
sudo apt install lsb-release
At the time of this writing, Docker does not yet support the noble codename. Instead, you must temporarily use jammy (Ubuntu 22.04 codename) when adding the repository.
Use the following script to detect the codename and substitute jammy if needed:
# Get the Ubuntu codename
CODENAME=$(lsb_release -cs)
# Workaround: Docker does not yet support 'noble'
if [ "$CODENAME" = "noble" ]; then
CODENAME=jammy
fi
# Print it
echo $CODENAME
When the Docker starts supporting noble codename directly, only the first command from above will be needed.
Environment variable CODENAME now contains a working value and we will use it in the command to install Docker (see below).
Before Docker installation
Update the system
Make sure your system is up to date:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
Install required dependencies
Install the required packages before adding Docker’s repository:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common lsb-release -y
apt-transport-https: Access repositories over HTTPS.
ca-certificates: Validate SSL certificates.
curl: Download Docker’s GPG key.
software-properties-common: Manage external repositories.
lsb-release: Detect the OS codename.
Add Docker’s GPG key
Add Docker’s GPG key to ensure the integrity of downloaded packages:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/docker.asc
Add Docker’s Official Repository
Docker packages are distributed through codename-based repositories. We have captured the exact meaning $CODENAME so we now just use it. The following command creates a new repository file with Docker’s package source:
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $CODENAME stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list
That command will save the required information into the docker.list and the following commands will read it from there.
Install Docker engine
Now install Docker:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y
docker-ce: Docker Community Edition
docker-ce-cli: Command-line interface
containerd.io: Container runtime
Verify that Docker is installed and running
Enable and start Docker:
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl status docker
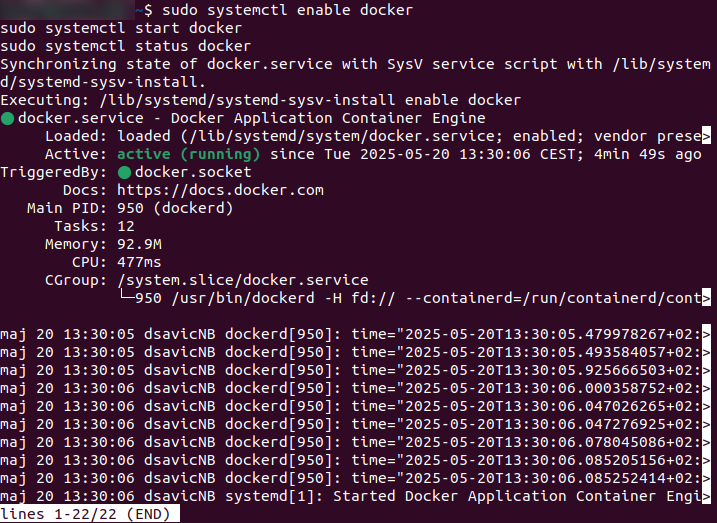
Press Ctrl-C to return to the prompt.
Verify Docker installation
Run a test container:
sudo docker run hello-world
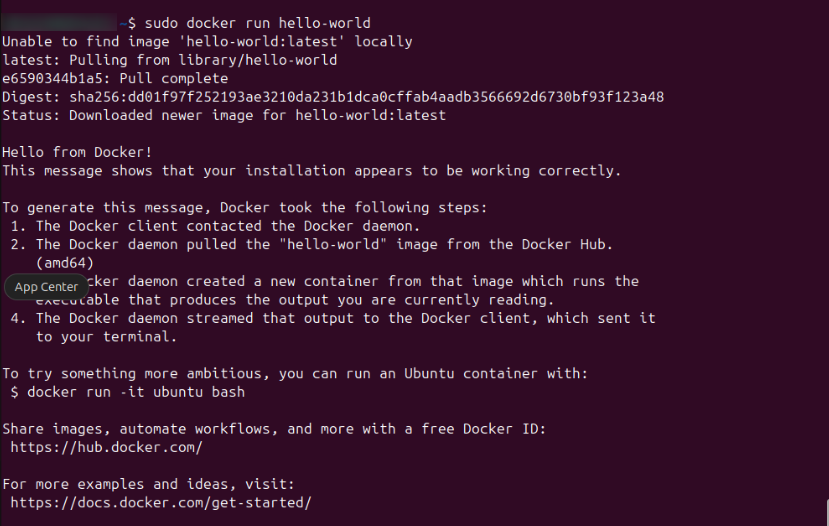
This confirms Docker is correctly installed. If errors occur, read the message carefully—it often includes the fix.
Basic Docker commands
Downloading Docker Images
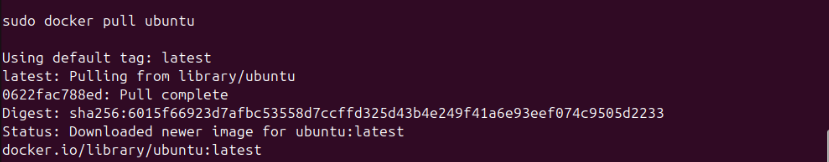
There are hundreds of thousands of Docker images to download. For this example, we choose to download the latest image of Ubuntu operating system. The command is:
sudo docker pull ubuntu
To view downloaded images:
sudo docker images
This shows available local images:

Running Docker Containers
You can run a container interactively. The actual commands will depend on the container downloaded; here, for Ubuntu image, we supply a command to start working within that Ubuntu container.
sudo docker run -it ubuntu

You now have a shell inside the container. The prompt for Ubuntu running inside a Docker container in our example is root@ab3f2a78046b:/# and it will, most probably, differ on your system.
Use commands like ls to explore the root directory. It will contain folders such as bin, dev, home, and other directories typical of a standard Ubuntu installation.
Managing Docker containers
Create a container (but don’t start it):
sudo docker create ubuntuStart an existing container:
sudo docker start <container_id>Enter a running container:
sudo docker exec -it <container_id> /bin/bashStop a running container:
sudo docker stop <container_id>Remove a stopped container:
sudo docker rm <container_id>
Listing Docker containers
List running containers:
sudo docker psList all containers (including stopped):
sudo docker ps -a
Other useful Docker commands
Remove a Docker image:
sudo docker rmi <image_id>List Docker volumes:
sudo docker volume lsView container logs:
sudo docker logs <container_id>
Troubleshooting
If Docker commands fail with permission denied:
Use sudo, or
Add your user to the docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERThen log out and log back in.
If docker run hello-world fails:
Check if Docker is running:
sudo systemctl status dockerView logs:
sudo journalctl -u docker
What To Do Next
Here are some articles that build upon this tutorial: